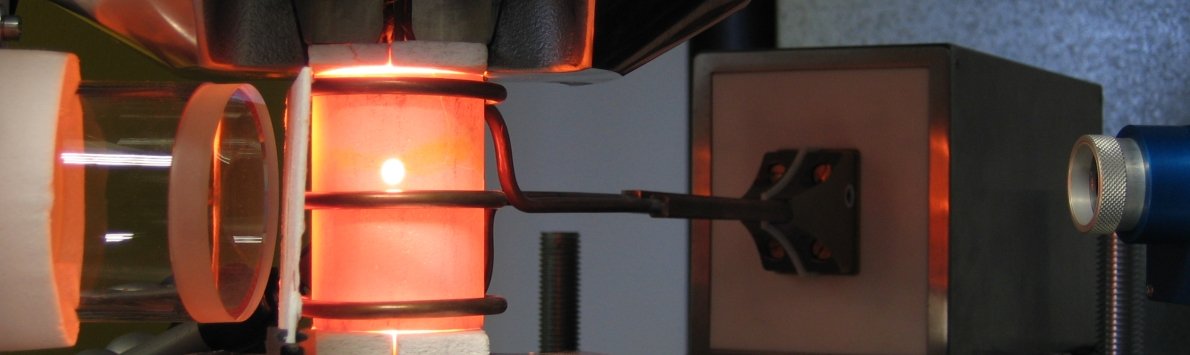
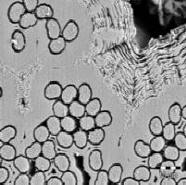
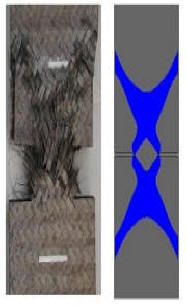
Advanced Ceramic Composites
Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMC) with fibre reinforcement or other composite materials as layered structures with stiff and weak components provide an exemplary way to increase the fracture toughness of engineering ceramics, while other superior properties of ceramic structures are retained. The behaviour of these composites is strongly dependent on the components used. A smart combination of reinforcement, interface and matrix materials leads to sophisticated composites achieving highest performances especially in severe environmental conditions. This enables the designing engineer to adjust the composite properties specifically to various application requirements and mechanical load conditions. The major scopes of ceramic composites can be divided into three areas: Advanced Ceramic Composites for biological applications (e. g. bioceramics), Advanced Ceramic Composites for room and high temperature applications and Advanced Ceramic Composites for applications in extremely corrosive environments. Beside oxidation and corrosion resistance, the mechanical properties of the composites as e.g. fracture toughness and damage tolerance are of major interest. Thus, the mechanisms being responsible for the damage tolerant behaviour have to be adjusted to achieve crack deflection and high energy dissipation in general. A focus lies in the investigation and interpretation of mechanical behaviour of ceramic fibre reinforced ceramic matrix composites (CMC). In all variations, whether short- or long-fibre reinforced, the interface or the matrix has to meet this challenge. In consequence, different CMC strategies have been followed, i.e. Weak Interface Composites (WIC) or Weak Matrix Composites (WMC). The WMC-concept is characterised by a fibre dominant behaviour, while the interface is of minor importance. The opposite case is followed by the WIC-concept which is governed by a weak interface taking also into account that the mechanical properties of the fibres (reinforcements) generally exceed the matrix properties. However, it has to be pointed out that these CMC strategies represent idealised models and the optimized performance is reached somewhere in between these concepts meeting the requirements of different applications. Research activities in this area are given below.